
TRUTH
Without truth, everything collapses.
Truth is not just a fact. It’s force. Also, it’s frequency.
It’s the vibration that aligns reality with potential.
In the Spiral Influence model, Truth is the code behind every transformation.
No Spiritual Intelligence (Si) without honesty.
Also, no Emotional Intelligence (Ei) without authenticity.
No Cognitive Intelligence (Ci) without clarity.
Further, no Moral Intelligence (Mi) without integrity.
Truth is the backbone of your Personal Truth Radius (PTR).
The wider your PTR, the more influence you command.
Brief tentacles of Truth
Figure 1: Philosophy Branches
Epistemology, metaphysics, logic, and axiology are the four primary branches of philosophy that deal with the pursuit of truth. The four categories of logic are as follows: deductive, inductive, abductive, and fallacy logics. Among the four branches, logic is the most important, as it gives the truth precision.
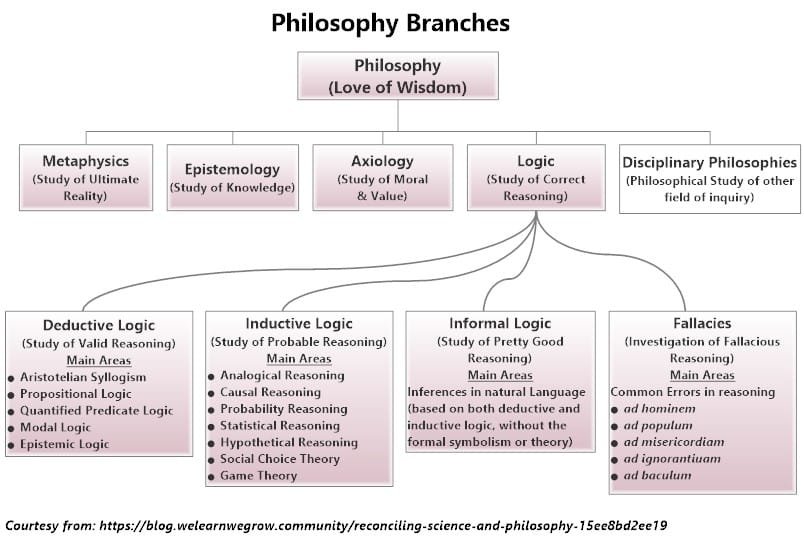
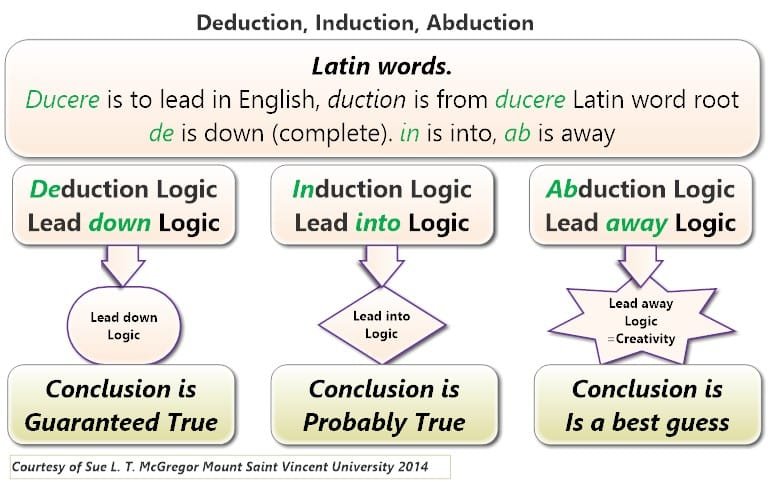
Figure 2: Compare deduction, induction and abduction
The three primary logic methods used in the pursuit of truth in philosophy are deduction, induction, and abduction. There is an assurance of a deduction-logic conclusion. The induction logic conclusion is probably true, and the abduction conclusion is a best guess. Fallacies are erroneous logics usually based on self-deceit.
But here’s the catch:
Truth starts within.
You can’t lead a team, build a brand, or influence a culture if you’re lying to yourself.
Your KCUE Engine—the driving force of your Ultimate Enterprise—only roars when it’s running on truth.
And when you speak your truth—even if your voice shakes—you do more than express.
You activate. Also, you awaken. and you shift.
Spiral Truth Test:
- Can your vision withstand truth?
- As well, can your team speak the truth?
- Can your influence hold truth without shattering?
If yes, you’re not just building a brand.
You’re building a legacy.
🧭 In a noisy world full of scripts and filters,
those who dare to tell the truth become the real influencers.
Want to build your Personal Truth Radius?
→ [Explore Your KCUE Map]
→ [Activate the PIS (Personal Influence Scanner)]

