
Strategy (Resource Allocation)
Strategy is the intentional allocation of resources to achieve a desired outcome—typically, delivering value to shareholders through a robust, well-aligned business model. Fundamentally, strategy is about making well-informed choices that promote long-term success, creativity, and financial gain. If a strategy fails to produce meaningful, consistent returns, it needs to be re-evaluated. A good strategy is not just about having a plan—it’s about choosing what to do, what not to do, and where to focus energy for maximum return.
A strategy is a blueprint for distributing resources to a manufacturing or assembly location. It serves as a way to deliver value to the organization’s shareholders, utilizing a robust business model made up of effective components. You can view an overview of the plan in the attached video.
“Strategy is simply resource allocation. When you strip away all the noise, that’s what it comes down to.” – Jack Welch:
Think of strategy as a blueprint for resource distribution—be it talent, time, finances, or technologies. This blueprint guides how resources flow to operational sites, product development teams, or market expansion initiatives.
Strategic thinking and strategic planning are distinct but interconnected:
- Strategic Thinking: A systemic, creative process that evaluates the big picture. It identifies patterns, evaluates trade-offs, and foresees potential opportunities or threats.
- Strategic Planning: Converts insights from thinking into actionable, trackable steps. It defines policies, procedures, and performance indicators.
Together, they form the foundation of strategic management—a continuous cycle of vision, alignment, execution, and renewal.
Key Visual Models of Strategy
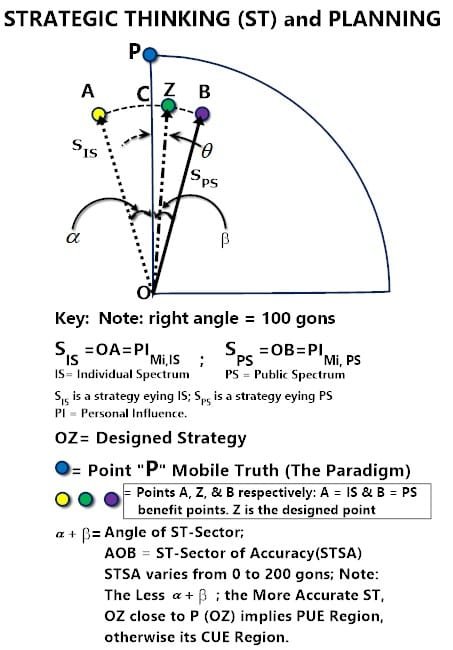
- Strategic Thinking and Planning Diagram (Figure 1): A dynamic model showing a Truth Point ‘P,’, which represents the optimal policy-driven strategy.
Figure 1: Strategic Thinking and Planning
Strategic Thinking and Planning Diagram showing a truth point ‘P’ defined by a policy. Point P is the desired strategic plan for both individual and public benefit. It is mobile, depending on the priorities. Pins A and B are dynamic, representing IS (individual benefits) and PS (public benefits), and are typically established by SOPs (standard operating procedures) or rules. Designed strategy: Point P must be within sector OAB.
- Closed Strategic Model (Figure 2): A static strategy model where the business model is fixed during execution.
Figure 2: Closed Strategic Model
A closed strategic model illustration shows systemic thinking and creative problem solving during strategic thinking and strategic planning. Strategic thinking and strategic planning together are called strategic management. A strategic model is closed when, during planning, there is no update to the business model.

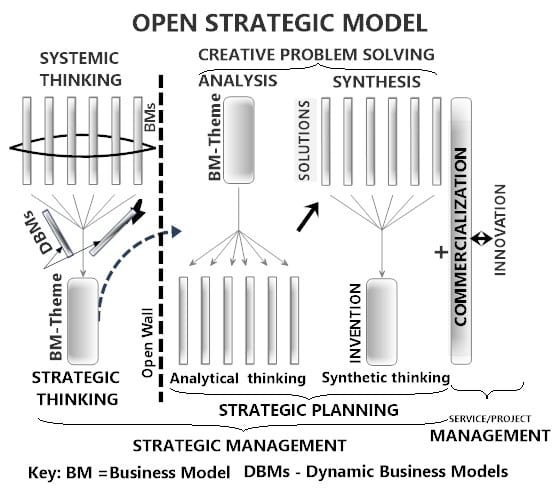
- Open Strategic Model (Figure 3): A dynamic strategy model that allows updates to the business model during execution.
Figure 3: Open Strategic Model
Open Strategic Model illustration showing systemic thinking and creative problem solving during strategic thinking and strategic planning. Strategic thinking and strategic planning together are called strategic management. A strategic model is open when, during planning, an update of the business model is allowed.
Business Models: The Engine Behind Strategy
Every effective strategy starts with a business model—a structural map of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value.
Core Characteristics of a Strong Business Model:
- Goal Alignment: Every decision should support the organization’s long-term mission.
- Self-Reinforcement: All parts of the model strengthen each other.
- Robustness: It must endure market pressures like competition, disruption, and internal inertia.
Core Business Model Functions:
- Customer Identification: Who are you serving, and what matters to them?
- Economic Logic: How do you deliver value in a way that’s efficient and profitable?
Strategic Models: From Vision to Action
Strategic models transform a business model into a roadmap for execution:
- Closed Strategic Model: Best for predictable, low variance environments.
- Open Strategic Model: Ideal for dynamic, complex markets requiring constant adaptation.
Both require alignment with your organization’s Spiritual (Si), Emotional (Ei), Cognitive (Ci), and Moral (Mi) intelligences—the core of the www.SpiralInfluensa.com model.
Conclusion: Strategy as the Backbone of Enterprise Thinking
An effective strategy connects vision to execution, aligning inner intelligence with external opportunity. It is the first critical link in the Ultimate Enterprise Model, guiding how resources are distributed, systems are designed, and outcomes are measured. Strategy isn’t just about competition. It’s about clarity, courage, and contribution.
Ready to go deeper?
🔗 Next Step: Explore the Synergy Link, where strategy meets collaboration, fuelling momentum through unified action.

