
Macro-Leadership (Organizational Leadership)
For any organization to thrive, leadership must function across all levels: micro, meso, and macro. Macro-leadership represents the highest tier—focused on aligning the organization with external environmental dynamics while staying true to its vision, mission, and objectives. It requires scanning broader systems and driving strategic adaptation and transformation from the top.
Macro-Leadership in Action: The Kuhn Cycle and Beyond
The Kuhn Cycle
Figure 1: Kuhn Cycle
Figure 1: Kuhn Cycle illustration showing five scientific periods of the Kuhn Cycle, viz., normal science, model drift, model crises, model revolution, and paradigm shift in a clockwise direction. Normal science is the beginning of applied science until it starts drifting. It continues to experience crises until a paradigm shift occurs after a revolution.
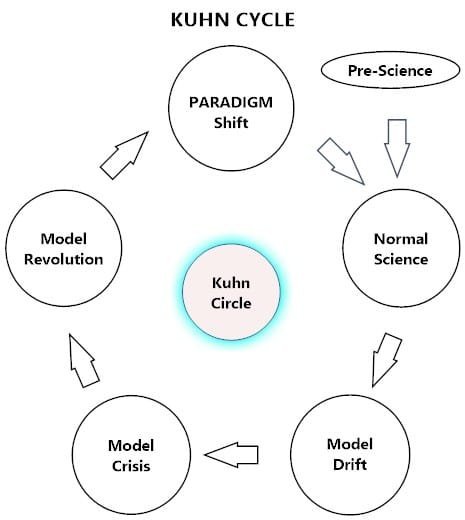
The Kuhn Cycle, a foundational concept in the philosophy of science, outlines five key stages of scientific evolution:
1 Normal Science
2 Model Drift
3 Model Crisis
4 Model Revolution
5 Paradigm Shift
These stages describe how scientific paradigms evolve—not linearly, but through cycles of disruption and renewal.
The Kuhn Cycle Ultimate Enterprise (KCUE)
Figure 2: Kuhn Cycle Ultimate Enterprise (KCUE)
Kuhn Cycle Ultimate Enterprise (KCUE) is an empowerment of the Kuhn Cycle. From Kuhn-Cycle, two periods were added. The first is between normal science (invention) and model drift (anomalous), called innovation (puzzle solving or creation), and the second between model drift (anomalous) and model crises, called recuperation (or fail).
From these additions, two important cycles result, viz., the virtuous cycle (Vir-Cycle) and the vicious cycle (V-Cycle). Vir-cycle is the opposite of v-cycle; Vir-cycle is the product of PUER management, and V-cycle is from CUER. In either cycle, they follow distinct and unique loops; a loop from the V-cycle, if governed in the Vir-cycle, is an incumbent retard in the V-cycle.
However, if a loop from Vir-cycle is implemented in V-cycle, the loop won’t work, implying an incumbent remains in V-cycle. There are two chances for a V-cycle organization to ascend into Vir-cycle: at model anomalous to re-model towards Vir-cycle, or at model crises to re-engineer the loop. See details in the eBook (Spiral Influence: The Modern Blueprint for Business Growth and Leadership)

The Kuhn Cycle Ultimate Enterprise (KCUE) expands on the original model by introducing two additional stages:
– Innovation
– Recuperation
These additions form the foundation for two strategic cycles:
– Virtuous Cycle (Vir-Cycle): Driven by PUER (Pro-Ultimate Enterprise Region)
– Vicious Cycle (V-Cycle): Driven by CUER (Contra-Ultimate Enterprise Region)
Ultimate Enterprise Thinking (UE-Thinking)
UE-Thinking empowers macro-leadership through two strategic lenses:
1. Big-Picture Thinking
2. Systemic Thinking
Together, they form Ultimate Enterprise Thinking—the cognitive framework for high-level strategic leadership.
Understanding the Paradigm
Thomas Kuhn defined a paradigm as both a community’s shared constellation of values and a set of puzzle-solving models. In KCUE, leadership must decode which paradigm their organization operates within—and decide whether to maintain it, challenge it, or reinvent it.
Three Cycles of Organizational Growth
1. Kuhn Cycle
2. Virtuous Cycle (Vir-Cycle)
3. Vicious Cycle (V-Cycle)
System Thinking for Macro-Leaders
Creative Thinking includes:
1. Creative Systems Thinking
2. Creative Human Thinking
Lean Logical Thinking (LLT) is a structured approach to understanding processes and making informed decisions.
Power in Organizational Context
Power is an individual’s relative competence to change others by providing or withholding resources or administering punishments…both material and social.
High-Performance Politics
Organizational politics becomes strategic when governed by PUER. Leaders must embrace their political role to manage power, resolve conflicts, and influence change.
The Leader as Politician (Personality Tetra-Receptor)
Leaders operate through the Personality Tetra-Receptor (PTR):
– Spiritual Receptor
– Emotional Receptor
– Cognitive Receptor
– Moral Receptor
Global Leadership & Cultural Intelligence
Understanding culture is a critical skill for global leadership. Culture includes values, symbols, traditions, and actions.
Cross-Cultural Dimensions (Geert Hofstede)
Especially Power Distance:
– Small Power Distance (PUER): Democratic, transparent
– Large Power Distance (CUER): Autocratic, centralized
Conclusion: The Macro-Leader’s Challenge
To lead at the macro level is to act as:
1. Visionary
2. System Thinker
3. Politician
4 Cultural Navigator
The KCUE model empowers organizations to evolve—choosing virtue over survival, innovation over stagnation, and sustainable power over fear-based control.

