
Innovation: The Engine of the Virtuous Cycle
Innovation refers to the continuous thinking and practice that maintains an enterprise in a virtuous cycle. Following discovery and invention, innovation is the strategic implementation that transforms potential into actionable outcomes. At Spiral Influensa, Innovation, Invention, and Discovery are viewed as an interconnected triad, each supporting the other within the Ultimate Enterprise Model.
R&D Is Not Enough Without Innovation
Business is inherently complex. Organizations can falter without proper R&D orientation. Rigorous research must be aligned with relevant attributes to ensure valuable outcomes. There is no strict division between the roles of inventor and innovator. Individuals or enterprises often navigate through discovery, invention, and innovation stages to address problems and remain competitive. Embracing this fluid movement provides competitive advantages.
Visualizing Innovation in the UE Model
Figure 1: R&D as a Prime Union for Ultimate Enterprise
R&D as A Prime Union for Ultimate Enterprise
Figure 1: R&D as a Prime Union for Ultimate Enterprise illustrates the role of R&D in all footage of Ultimate Enterprise. Empowering Footage (synergy and SIA links), Business Footage (leadership, strategy, and management links), and Enlivening Footage (Personal Reinvention). The diagram shows the significance of the three footages; without it, all footage collapses.

This diagram illustrates how R&D supports various aspects of the Ultimate Enterprise:
- Enlivening Footage – Personal Reinvention
- Business Footage – Leadership, Strategy, and Management
- Empowering Footage – Synergy and SIA
Without R&D, these areas diminish. With R&D, they form a thriving ecosystem.
Discovery → Invention → Innovation
Figure 2: The Discovery, Invention, and Innovation Relationship
Figure 2: Discovery, Invention, and Innovation Relationship
The Discovery, Invention, and Innovation relationship diagram shows the R&D amplification on the three footages: enlivening footage (as workforce, business footage, leadership, strategy, and management), empowering footage (synergy, and SIA).
The discovery level is an identification of links along the footage, viz., enlivening (personal reinvention) if the workforce is desirable, business (leadership, strategy, and management) if viable, and empowering (SIA and synergy) if serene. The invention level is finding empowering themes between footage. Enlivening with business footages must be empowered emotionally (motivating leadership, strategy, and management). Businesses with empowering footage must be empowered in process (finding the best process in leadership, management, and strategy, e.g., work-study). Enlivening with empowering footage must be empowered functionally (finding the best function personnel, e.g., personal Noble Touch, or otherwise).
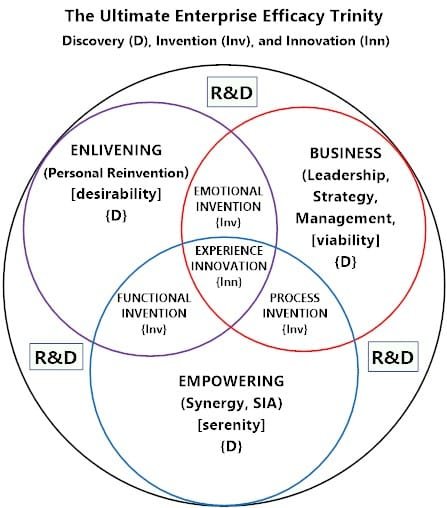
This model shows how each stage contributes to the three UE footages:
1. Discovery
- What is desirable? → Enlivening Footage (Workforce, Personal Reinvention)
- What is viable? → Business Footage (Leadership, Strategy, Management)
- What is serene? → Empowering Footage (Synergy, SIA)
2. Invention
- Emotional Empowerment between Enlivening & Business
- Process Empowerment between Business & Empowering
- Functional Empowerment between Enlivening & Empowering
This tri-footage approach transforms organizations into Ultimate Enterprise Engines.
Figure 3: The Design Thinking Process
Figure 3: Design Thinking Process
The Design Thinking Process diagram is a way of thinking depicted in Figure 1, calling for powerful creativity. It is a continuous thinking process of the past, the present, and the future. The past represents self-respect, present self-confidence, and future self-belief. MSIA (Multi-Sensory Inference Activity) and P2MSI (Professional Profile Multi-Sensory Inference) are the thinking processes in creative imagination. For details, refer to the Spiral Influence – The Modern Blueprint for Business Growth and Leadership eBook.
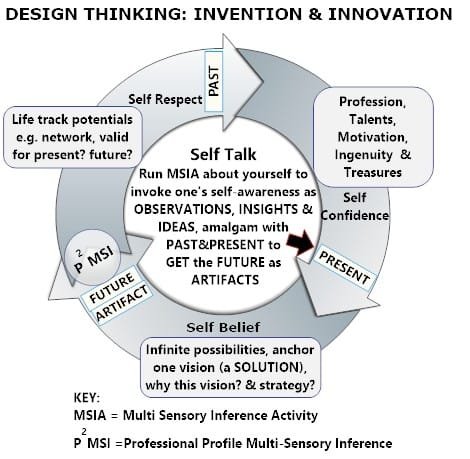
This visual reflects the cyclical and imaginative thinking process essential to innovation:
- Past → Self-Respect
- Present → Self-Confidence
- Future → Self-Belief
MSIA (Multi-Sensory Inference Activity) and P2MSI (Professional Profile Multi-Sensory Inference) are models for activating creative imagination and innovation.
(Refer to the Spiral Influence – The Modern Blueprint for Business Growth and Leadership eBook for detailed methodology.)
Discovery, Invention, and Innovation in Action
Apple Inc. discovered and invented the iPhone’s design. Samsung replicated aspects of the invention and faced global legal battles. This example demonstrates that innovation, guided by R&D ethics, delivers a significant competitive advantage.
Five Core Innovation Types
(as cited from the Oslo Manual & Gary Hamel1)
| Innovation Type | Description |
| Product Innovation | Enhancing functionality, software, materials, or user experience |
| Process Innovation | Introducing new production or delivery methods |
| Marketing Innovation | Innovating branding, pricing, packaging, or promotions |
| Organizational Innovation | Creating new business structures or practices |
| Management Innovation | Rethinking how managers lead and operate |
🧠 These innovation types are measurable, practical, and drive modern business strategies.
🌀 Intangible Innovation
Modern enterprises must shift from traditional physical products to experiential and knowledge-driven innovation:
Emotional Design
Service Intelligence
User Empowerment Systems
This transition showcases the true power of Spiral Influensa, blending inner intelligence with enterprise design.
🔬 Table 1: Invention vs. Innovation
| Aspect | Invention | Innovation |
| Where | Research centres, academia, SMEs | Enterprises focused on commercialization |
| Who | Inventor – curious, conceptual mind | Innovator – adaptive, risk-taking executor |
| Role Profile | Combines original ideas | Merges inventions with markets, technology, and strategy |
Source: i3e.eu
Experience Innovation (ExI): Transforming Business through Meaningful Engagement
The New Era of Business Innovation
Experience Innovation (ExI) represents a contemporary business strategy focused on trust, stakeholder engagement, and immersive value creation. Unlike traditional innovation, which concentrates on products and services, ExI incorporates experiential elements across all components of business—enhancing customer interactions, brand loyalty, and long-term success. At its core, Experience Innovation is centered on co-creation, involving customers not merely as consumers but as active participants in shaping their own experiences.
According to Juha Oksanen et al., citing Pine and Gilmore, “An experience occurs when a company uses services as the stage—and goods as props—for engaging individuals in a manner that creates a memorable event.” This shift in paradigm positions businesses as storytellers, where products and services embody customer narratives.
The Role of R&D in Experience Innovation
In the Ultimate Enterprise Model, R&D serves as the universal enabler that integrates various business elements into a cohesive experience. Figure 1: R&D as a Prime Union for Ultimate Enterprise illustrates how research and development connect three significant business narratives:
- Enlivening Story – Focused on Personal Reinvention
- Business Story – Encompassing Leadership, Strategy, and Management
- Empowering Story – Covering Synergy and Social Impact Assessment (SIA)
These three dimensions form the UE-Efficacy Trinity, aligning discovery, invention, and innovation into a unified framework that propels sustainable growth.
The Experience Innovation Framework
Experience Innovation synthesizes three fundamental business aspects:
- Enlivening (Personal Reinvention – People): The human component, fostering transformation and adaptability.
- Business (Leadership, Strategy, Management): The structural and operational foundation.
- Empowering (Synergy, R&D, SIA): The mechanism ensuring efficiency, impact, and sustainability.
Miscovich and Peter’s model aligns with this perspective, incorporating technology as an empowering factor that bridges these dimensions.
1. Personal Reinvention (People)
People are the driving force of innovation. Their transformation from passive participants to engaged contributors determines the success of Experience Innovation. The Personal Influence Scanner (PIS) helps organizations evaluate whether individuals operate in the Pro-Ultimate Enterprise Region (PUER) (optimal performance) or Contra-Ultimate Enterprise Region (CUER) (detrimental to innovation). Invention and innovation require both cognitive and spiritual intelligence. A deficiency in either leads to weakened design thinking capabilities. The Self-Talk + Experience + Present Opportunities Route is a guiding process for innovation, ensuring meaningful customer engagement.
2. Business (Leadership, Strategy, and Management)
Business structures and systems must be designed for innovation. The role of R&D in business is to harmonize components—ensuring that market-ready products empower society. Strategic planning and business modelling must align with innovation goals to sustain long-term growth. The Lean Management approach ensures a continuous improvement cycle, reducing inefficiencies and maximizing value.
3. Empowering (Synergy & Social Impact Assessment – SIA)
Synergy is the bridge between business operations and societal impact. Organizations must ensure that innovations benefit both internal teams and external stakeholders. Synergies must be designed intentionally, avoiding common failures caused by poor design, timing, and selection. R&D must scrutinize all potential innovations to ensure organizations operate at optimal efficiency.
The Three Pillars of Experience Innovation
1. Emotional Invention (EIN)
Emotional Invention differs from Emotional Intelligence (EI). It refers to an enterprise’s ability to manage emotions in business environments. Businesses must monitor and mitigate negative emotions while fostering positive emotional engagement. Market trends, consumer sentiment, and cultural shifts influence business adaptation.
2. Process Invention (PI)
Process Invention (PI) ensures continuous operational improvement. PI is a core element of Lean Business and Strategic Performance. Organizations must innovate how they operate, not just what they offer. Businesses with misaligned strategy and execution risk losing competitive advantage.
3. Functional Invention (FI)
Functional Invention evaluates how well synergistic methods empower businesses and individuals. Many organizations fail to leverage existing synergies due to lack of clear design thinking. Example: The blend of computers and the Internet has unlocked vast opportunities, yet some businesses still underutilize them.
Experience Innovation as the Ultimate Competitive Advantage
Experience Innovation is the next frontier of R&D. It aligns all six UE-Model links, ensuring innovation is controlled and strategic. ExI is not optional—without it, long-term success is at risk. Nations such as China are investing heavily in R&D, recognizing innovation as a global competitive driver.
The Future of Experience Innovation
Research and Development (R&D) is the foundation of Experience Innovation. ExI transforms businesses from product-focused entities to experience-driven ecosystems. Organizations that master experience innovation will lead the future economy. This marks the conclusion of the Research & Development Link and the final link in the Ultimate Enterprise Model.
🧭 Final Insight: Innovation
To stay in a virtuous enterprise cycle, one must innovate continuously—with intention, alignment, and creativity.
Innovation is the pulse. R&D is the compass. Ultimate Enterprise is the journey.
- Oslo Manual: GUIDELINES FOR COLLECTING AND INTERPRETING INNOVATION DATA, Third Edition; A joint publication of OECD and Eurostat © OECD 2005 ↩︎
